The AI Executive Brief - Issue #18
Week of February 2, 2026
This week in AI was marked by significant steps in agentic systems and major industry consolidation. Anthropic released Claude Opus 4.6, introducing multi-agent team capabilities and a one-million-token context window, presenting a move toward more complex, autonomous AI workflows. In a landmark $200 million deal, OpenAI and Snowflake partnered to embed AI agents directly into enterprise data platforms, aiming to accelerate autonomous operations within governed data environments.
In a move that reshapes the AI infrastructure landscape, SpaceX acquired xAI in a deal valued at $1.25 trillion, uniting space technology with AI development. The acquisition aims to leverage orbital platforms for low-cost, large-scale AI computation. Concurrently, the International AI Safety Report 2026 highlighted rapid advances in AI reasoning for mathematics and coding but also warned of increasing risks in autonomous systems and the potential for investment to slow if revenue generation does not follow suit.
Strategic Deep Dive
The Rise of Agentic AI Ecosystems
The most significant trend this week was the advancement of agentic AI systems, which are capable of autonomously executing complex, multi-step tasks. Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.6 is at the forefront of this shift, introducing a “multi-agent” collaboration feature. This allows specialized AI agents to work in parallel on large-scale projects, such as financial analysis or software development, supported by a one-million-token context window for processing extensive datasets.
Complementing this, OpenAI’s $200 million partnership with Snowflake will integrate AI agents into enterprise workflows through the new Frontier platform. This collaboration enables the deployment of AI agents within secure, governed data environments, transforming static databases into dynamic intelligence layers capable of multimodal analysis across both structured and unstructured data.
Business Implications and Competitive Dynamics
These developments are set to lower the barriers to enterprise AI adoption, enabling a shift from small-scale pilot projects to full-scale production implementations. Companies like Snowflake are gaining a competitive advantage by embedding AI capabilities natively into their platforms. This trend could disrupt the traditional Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) market as agentic systems begin to automate complex workflows in areas such as marketing, legal, and customer support. The rivalry among leading AI labs, including Anthropic, OpenAI, and Google, is intensifying, with differentiation now hinging on factors like safety, integration speed, and cost-efficiency.
Operational Risks and Value Creation
While the potential for value creation is immense, with some analysts projecting significant efficiency gains in knowledge work, the operational risks are equally substantial. The International AI Safety Report 2026 emphasizes the risks associated with data governance, as AI agents with access to sensitive enterprise data could amplify cybersecurity vulnerabilities. The report calls for robust refusal evaluations and safeguards for long-horizon tasks. On the value side, these systems have the potential to automate research and development pipelines, which could unlock trillions of dollars in productivity by 2030.
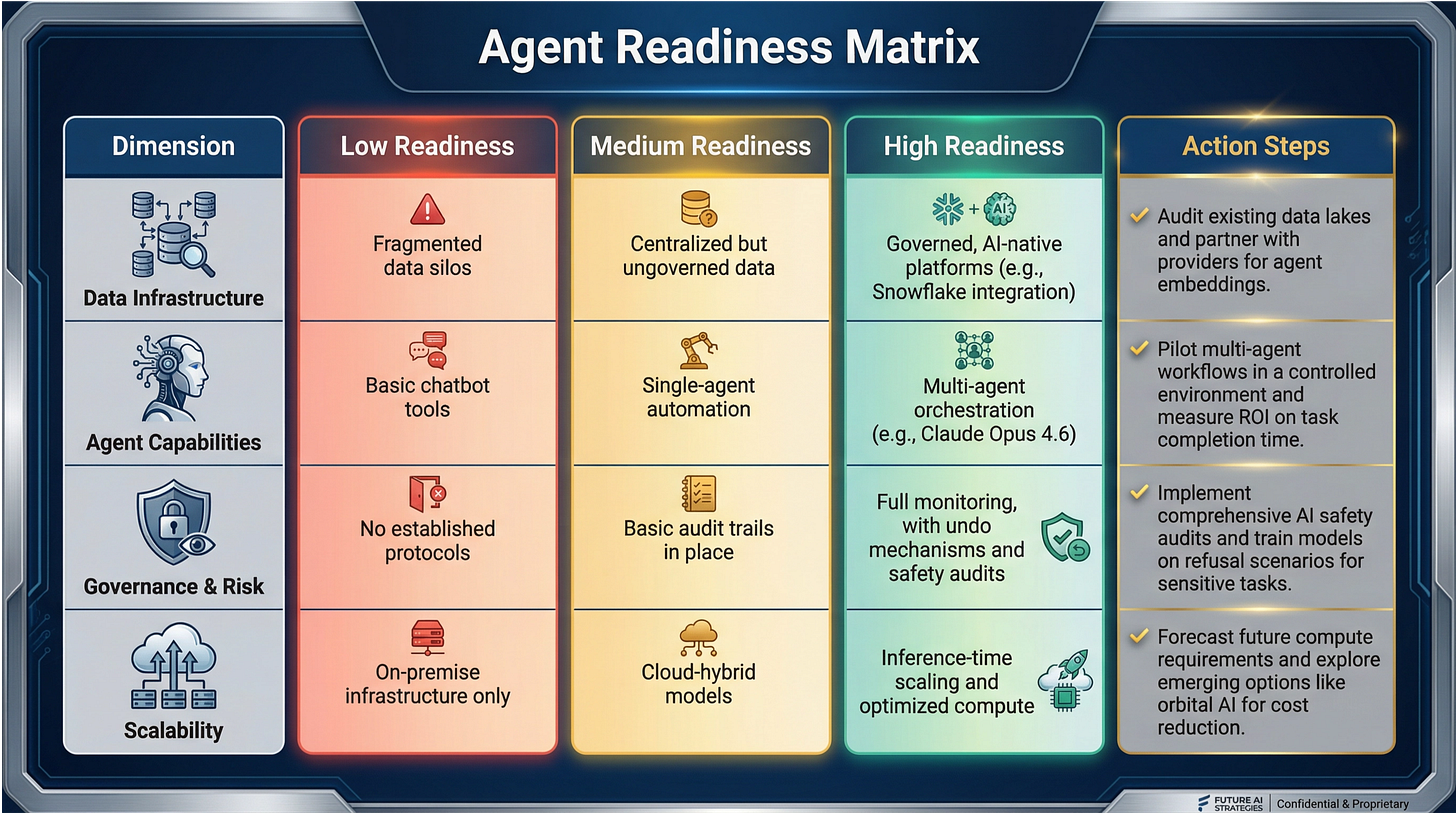
Framework for Executive Planning: Agent Readiness Matrix
To guide the adoption of agentic AI, executives can use the following Agent Readiness Matrix to assess their organization’s preparedness:
This matrix provides a framework for a phased adoption strategy. Organizations should begin with pilots in medium-readiness areas and scale to high-readiness implementations as the technology matures and internal capabilities improve.
SpaceX’s Acquisition of xAI and the Future of Orbital AI Compute
Elon Musk has consolidated his space and AI ventures with SpaceX’s acquisition of xAI. This deal merges rocketry, satellite networks (Starlink), and AI (Grok), with the ambitious goal of developing space-based AI compute infrastructure to significantly reduce costs within the next 2-3 years. The plan involves leveraging solar-powered satellites for AI training, thereby bypassing terrestrial constraints such as energy and land availability.
Business Implications and Competitive Dynamics
The acquisition creates a vertically integrated powerhouse that could dominate the AI infrastructure market by making compute power exceptionally cheap. This poses a significant challenge to established players like Nvidia and CoreWeave, as orbital systems could undercut the cost structure of traditional data centers, sparking a new race for space-AI hybrid solutions.
Operational Risks and Value Creation
The primary risks associated with this venture include regulatory hurdles, the high failure rate of space-based hardware, and ethical concerns surrounding the potential militarization of AI. However, the value proposition lies in the potential for exponential scaling. Cheaper compute power would accelerate breakthroughs in scientific research and autonomous systems, creating billions of dollars in efficiency gains for industries such as telecommunications.
Framework for Executive Planning: Compute Horizon Model
Executives should consider the following Compute Horizon Model to prepare for the shift in AI infrastructure:
Short-Term (1 Year): Optimize current terrestrial AI workloads and continue investing in hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Medium-Term (2-3 Years): Begin exploring partnerships for satellite access and conduct pilot projects for space-based inference.
Long-Term (5+ Years): Develop a comprehensive orbital AI strategy to diversify from ground-based infrastructure and mitigate long-term risks.
Leadership Action Playbook
To navigate the AI landscape following this week’s developments, executives should focus on integrating agentic systems while strengthening their organization’s defences.
Capitalize on Agentic Opportunities: Deploy multi-agent pilots using Claude Opus 4.6 or OpenAI’s Frontier platform in a core business function (e.g., R&D, operations) within the first quarter of 2026. Set a target of achieving a 15-20% efficiency gain by the third quarter and benchmark performance against the capability metrics outlined in the AI Safety Report 2026.
Mitigate Risks: Conduct a “Shadow AI Audit” to identify any unauthorized use of AI agents within the organization. Implement a robust governance framework that includes undo capabilities and detailed audit logs, drawing on the safety testing principles from Anthropic.
Accelerate Readiness: Form cross-functional “AI Fusion Teams” composed of members from technology, legal, and strategy departments to explore emerging opportunities, such as partnerships related to space-based AI. Begin upskilling at least 20% of the leadership team on agentic systems through targeted simulations and workshops. Monitor compute costs quarterly to prepare for the potential transition to orbital infrastructure and maintain a competitive edge.
Executive Perspective
As artificial intelligence evolves from generative tools into autonomous agents, we are witnessing a fundamental paradigm shift. Intelligence is no longer merely augmented; it is becoming an infrastructural component, embedded within data platforms and even orbiting the Earth. This week’s announcements from Anthropic, OpenAI, and SpaceX underscore a critical reality, the next phase of the AI race is about controlling the entire ecosystem.
Winners in this new era, such as the alliances formed by OpenAI and Snowflake or the consolidated empire of Elon Musk, could dictate the terms of economic abundance and potentially exacerbate existing inequalities. Leaders must view these developments as strategic imperatives. The key to success will be embracing agentic AI to unlock exponential value while vigilantly addressing the associated safety and governance gaps. In this environment, foresight is not just an advantage; it is the ultimate moat protecting against obsolescence.